How Hybrid Cars Work
Due to its capacity to combine the advantages of conventional petrol engines with the effectiveness and environmental advantages of electric power, hybrid automobiles have grown in popularity over the past several years. The automotive industry has been completely transformed by this ground-breaking technology, which provides a cleaner and more economical replacement for conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. We will examine the inner workings of hybrid vehicles in this post, as well as How Hybrid Cars Work and what makes them an effective and ecological means of transportation.
What is Hybrid Technology
Hybrid technology is an inventive and cutting-edge method of propulsion for cars that combines two or more separate power sources. Hybrid technology’s main goals are to maximise fuel economy, lower emissions, and improve all-around vehicle performance. This is accomplished by smoothly combining internal combustion engines—typically powered by petrol or diesel—with one or more electric motors, frequently in conjunction with a high-voltage battery pack and sophisticated control systems.
Depending on the driving conditions and the energy management system of the car, the internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors in a hybrid vehicle can operate together or separately. The battery pack, which stores electrical energy produced while driving or during regenerative braking, powers the electric motor. The electric motor can take over during low-speed, stop-and-go, or light-load driving, reducing or eliminating the requirement for the petrol engine thus conserving fuel and cutting emissions. In contrast, the internal combustion engine can deliver the required power in conditions involving high speed or heavy loads, ensuring the vehicle maintains performance while limiting fuel consumption.

Hybrid technology’s fundamental idea is to maximise the utilisation of both power sources to create the best possible balance between fuel efficiency and performance, hence minimising the vehicle’s environmental effect. Over time, this technology has developed into many hybrid system types, such as mild hybrids, full hybrids, and plug-in hybrids, each of which offers differing degrees of electric-only driving capabilities and fuel efficiency. In line with the global movement for lower carbon emissions and higher energy efficiency in the automobile sector, hybrid technology provides a significant step towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable transportation options.
Types of Hybrid Cars
There are three types of Hybrid car technology which are as follows:
Full hybrid (FHEV)
In full hybrids, the combustion engine is replaced by the battery for short bursts of electric propulsion. Fuel usage and exhaust pollutants are reduced as a result.
Either the battery or the engine provides power to the electric motor. Full hybrids, like mild hybrids, self-charge by recovering energy lost during braking or driving.
Mild hybrid (MHEV)
The car is always propelled by its engine, with the help of a strong electric battery, for example when accelerating. The engine’s duty is reduced by this battery boost. The battery is recharged using energy that would otherwise be wasted when braking.
Since mild hybrids are the most basic sort of hybrid, they often have poorer fuel efficiency and exhaust pollutants.
Plug-in hybrid (PHEV)
Plug-ins advance true hybrid technology because they both self-recharge and can be recharged by an external power source.
PHEVs offer a longer all-electric range than a complete hybrid due to their larger batteries. But their purchase price is likewise higher.
How Hybrid Cars Work
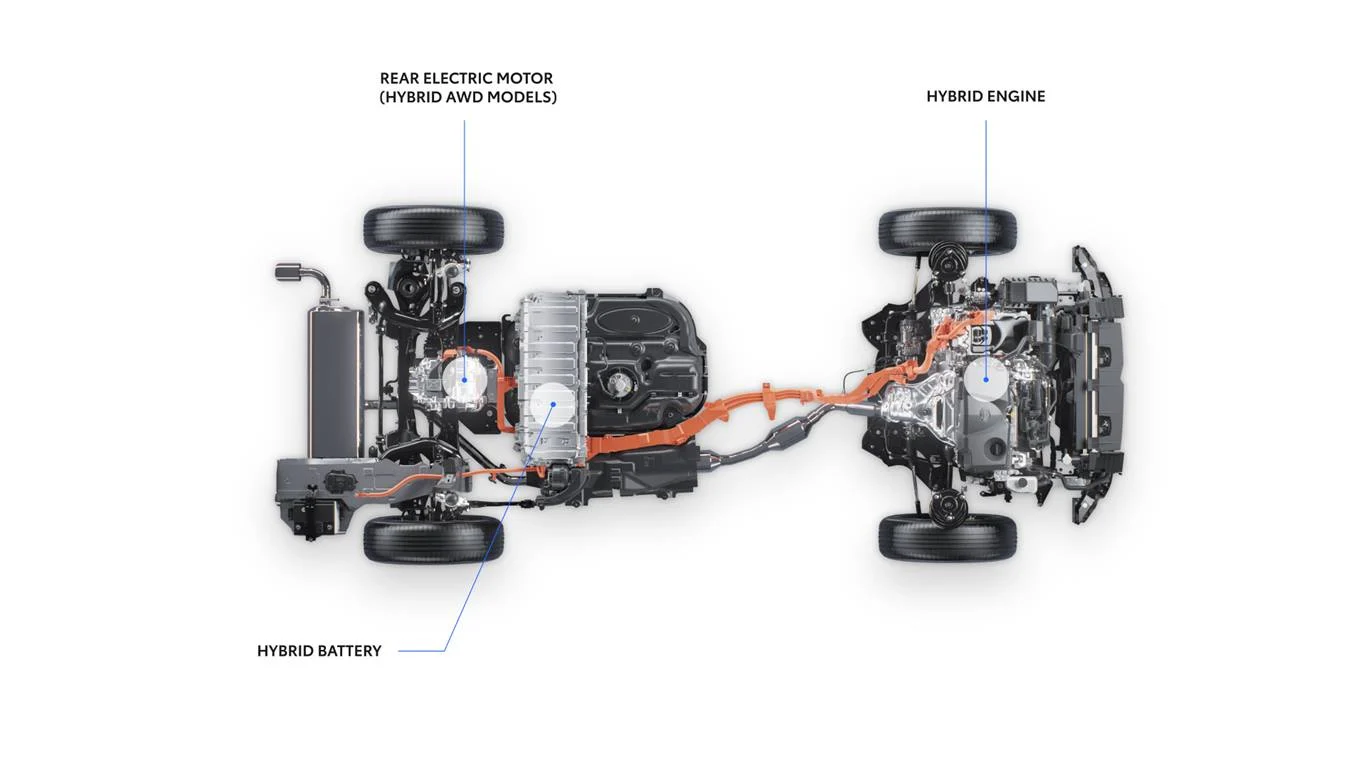
Components of hybrid powertrains
In hybrid vehicles, an internal combustion engine (which is commonly powered by petrol) and an electric motor are the two main power sources. These elements cooperate in a number of ways to enhance fuel economy and lower pollutants. Let’s examine the essential elements of a hybrid powertrain:
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE):
An ICE in a hybrid vehicle functions similarly to a standard petrol engine. It generates electricity by burning petrol, which powers the wheels of the car and replenishes the battery bank.
Electric Motor:
Vehicles that use hybrid technology have one or more electric motors. These motors can add extra power to the internal combustion engine and are fueled by a high-voltage battery pack. In rare circumstances, low-speed electric motors can independently move the vehicle.
Battery Pack:
The battery pack, which stores electrical energy for the electric motor(s), is an essential part of hybrid vehicles. These battery packs are made to be light and energy-dense and are often lithium-ion.
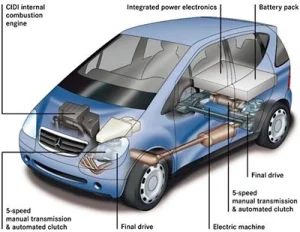
Power Electronic:
The flow of electricity between the battery pack, any electric motor(s), and the internal combustion engine is managed by power electronics, which includes inverters and converters. They control electricity distribution to increase effectiveness.
System of regenerative braking:
Regenerative braking is a common feature in hybrid vehicles. The electric motor(s) function in reverse when the brakes are applied to transform kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then saved in the battery pack. The battery is recharged throughout this procedure, which also improves productivity.
Modes of Operating
Hybrid cars employ a variety of operating modes to increase fuel economy and cut pollution. The main operational modes are as follows:
Electric Mode:
In this setting, the battery pack provides all of the vehicle’s energy needs as it runs entirely on electricity. This is primarily utilized for brief journeys at modest speeds.
Gasoline Mode:
In petrol mode, the car is powered by the internal combustion engine, which also recharges the battery pack. When greater power is needed and operating at faster speeds, this mode is employed.
Combined Mode:
To maximize performance and fuel economy, hybrid vehicles frequently combine the power of an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors. Depending on the road’s circumstances and the driver’s input, the system shifts between modes automatically.
Benefits of Hybrid Cars
Improved Fuel economy:
When compared to conventional petrol vehicles, hybrid automobiles provide a much higher fuel economy. Having the option to switch between electric and petrol power lowers fuel use and greenhouse gas emissions.
Lower Emissions:
Hybrid vehicles reduce their emissions and help to maintain cleaner air in cities by using electric power while travelling at a slow pace or in stop-and-go traffic.
Regenerative Braking:
This type of braking system increases effectiveness while also extending the useful life of the brake parts, which lowers maintenance costs.
Quiet Operation
Electric motors operate quietly, making driving more relaxing, especially when the vehicle is in electric mode.
Incentives:
To promote the use of hybrid vehicles, several governments and municipalities provide tax credits and incentives for their purchase.
Conclusion
As a middle ground between conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and totally electric automobiles, hybrid cars have evolved. They provide better fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and a more ecologically friendly driving experience because of their dual power sources and cutting-edge technology. Hybrid vehicles are anticipated to become increasingly more effective and appealing to people who care about the environment as technology advances. Hybrid vehicles are significantly lowering the carbon footprint of our transportation systems because of the automotive industry’s continuing focus on sustainability.






2 Comments