What Is Lane Assist In Car And How Does It Work
Introduction
A major increase in advanced driving-assistance systems (ADAS) research and integration has been observed recently in the automobile sector with the goal of improving driver convenience and safety. One such technology is Lane Assist, which is now a standard component in many contemporary automobiles. By assisting drivers in staying in their lane, Lane Assist lowers the chance of unintended lane exits and subsequent accidents. To make driving safer, we’ll explore What is lane assists in the car and how it works in this post.
What Is Lane Assist In Car And How Does It Work
What Is Lane Keep Assist In Car
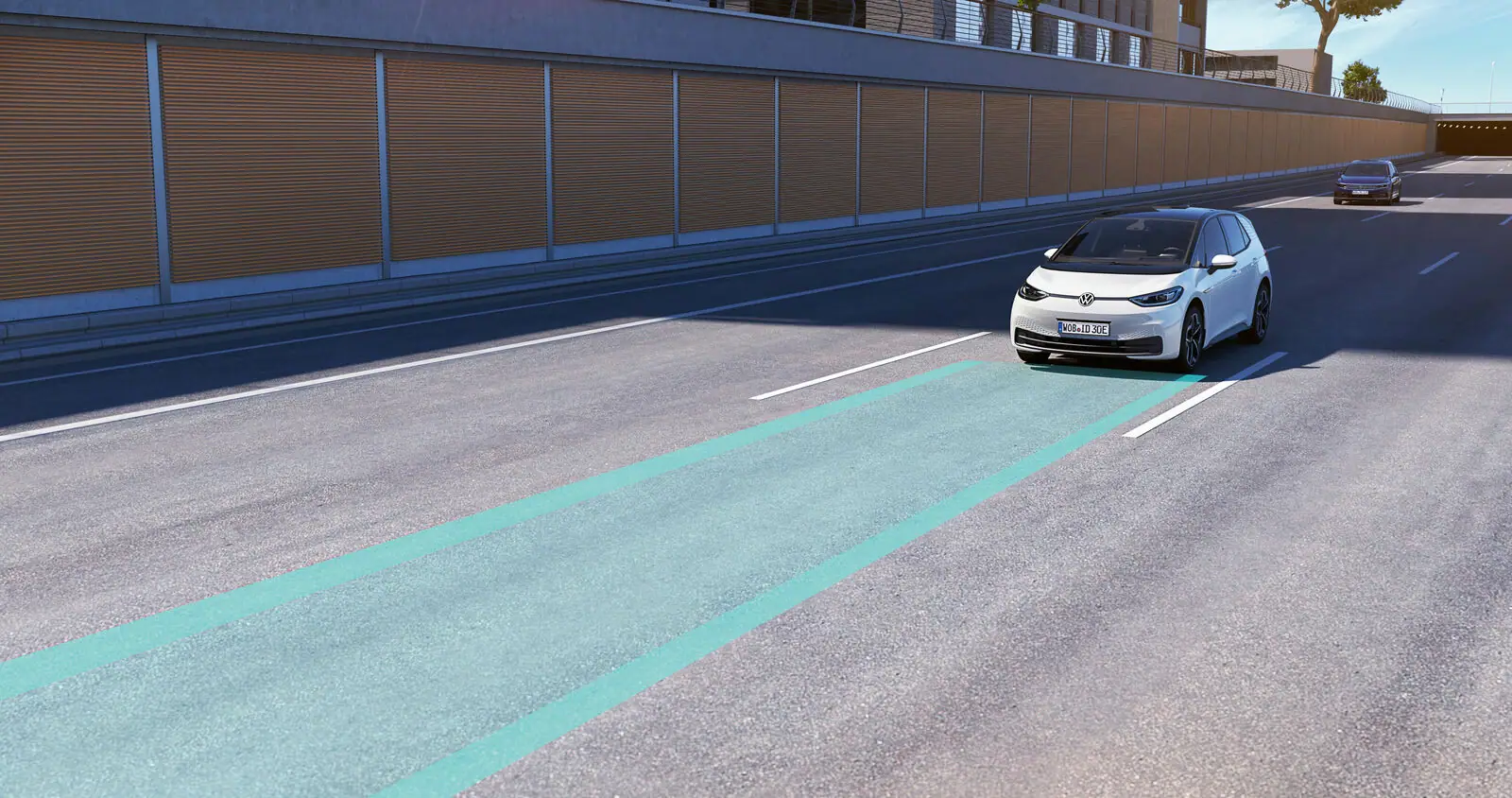
The Lane Assist feature, sometimes referred to as Lane Keeping Assist or the Lane Departure Warning System, is a crucial aspect of ADAS. Its purpose is to help drivers maintain adequate lane discipline by keeping track of a vehicle’s location inside its lane on the road. The main goal of lane assistance is to minimize accidental lane changes, which are frequently brought on by driver distraction, weariness, or inattention.

There are three different varieties of lane assistance. The first is the most traditional and is just an alarm system. This system keeps track of where you are in the lane and alerts you when you have veered off. The alarm might be felt as a vibration in the steering wheel, heard as a ding, or visible as a light on the dash.
More clever features include lane-keep assistance. Without using a turn signal, this technology can gently nudge your car back into the lane if you start to cross it.
The lane-centering assist feature is the most sophisticated. This technology centers you in the lane as well as keeping you there.
How Does Lane Assist Work
A lane departure camera, infrared sensors, and lasers are used as input devices in lane-assist technology. The camera is often located in the front or rearview mirror of the vehicle. In certain models, the camera is literally fixed to the rear of the car. The onboard computer can interpret the road lines that the camera codes into visual data in real-time. Instantaneously, this computer issues orders to actuators that warn the driver or direct the car back between the lines.
The device is useless if vision is impeded since the camera depends on visual input. Rain, snow, leaves, or deteriorated or badly painted road lines might all contribute to this. You cannot just rely on lane assist technology because of this.

To essentially read the road, Lane Assist employs a camera that is often installed behind the rearview mirror in your windscreen. In order to get your vehicle dead center, it considers the white lines on the far and near sides of your vehicle. The camera will alert you by emitting a tone or vibrating the steering wheel if it detects that you are in danger of veering too far to the right or left.
Camera Sensor:
A forward-facing camera installed on or close to the rearview mirror is the standard for Lane Assist systems. This camera continually records photos of the road ahead, including lane markings and nearby vehicles, continually.
Lane Detection:
In order to recognize lane markers, such as solid and dashed lines, the camera sensor analyses the pictures it takes. The system can recognize many kinds of road markers by employing image recognition and computer vision methods.
Vehicle Positioning:
Lane Assist locates the car within the lane once it has located the lane markers. The car’s lateral position in relation to the lane centerline is calculated.
Monitoring Driver Input:
Systems for lane assistance also monitor the driver’s steering movements. Lane Assist often doesn’t step in if the driver voluntarily switches lanes by activating the turn signal or using the steering wheel. However, the system intervenes if it notices an unintended lane deviation.
Waring Intervention:
The technology alerts the driver if it determines that the car is drifting out of its lane without the driver’s knowledge. This warning may appear as visual warnings on the dashboard, auditory alerts, or even vibrations in the steering wheel. Lane Assist may take remedial action if the motorist ignores the warning and keeps veering off the road.
Correction Mechanisms:
By providing corrective steering input to direct the car back into its lane, Lane Assist can help the driver. In order to promote a seamless and secure transition, this remedial intervention is often gradual and mild rather than sudden. In some cutting-edge systems, Adaptive Cruise Control and Lane Assist may combine to assist in maintaining the car centered in its lane while traveling along the highway.
User Customization:
Many lane assistance systems provide a variety of modification options, letting users change the sensitivity or turn off the function as needed. The system’s behavior is within the drivers’ control thanks to this flexibility.
Benefits Of Lane Assist
Improved Saftey:
Driving is safer for all users of the road because of Lane Assist’s ability to lower the risk of accidents brought on by unintentional lane exits.
Driver Assistance:
For drivers, lane assist is a useful tool, especially on lengthy highway drives or when weariness sets in.
Reduced Stress:
Driving stress can be reduced and driving confidence can rise when a driver is aware that Lane Assist is available to add an additional layer of safety.
Fuel Efficiency:
As it minimizes needless lane changes and harsh steering inputs, Lane Assist can also help to increase fuel economy by maintaining adequate lane discipline.

The amazing technology of lane assistance is a prime example of how ADAS is still developing in the automobile sector. Lane Assist systems improve driving comfort and road safety by integrating advanced sensors, cameras, and clever algorithms to assist drivers in staying in their lanes. Future vehicles will likely incorporate more refined versions of Lane Assist and other ADAS capabilities as the automotive industry develops, making our roadways safer for everyone in the process.
Conclusion
Let’s sum up by saying that Lane Assist technology is a fantastic development in driver assistance and automobile safety. Lane Assist is intended to actively monitor a vehicle’s location inside its lane and deliver corrective interventions as necessary by utilizing advanced cameras and sensors. By lowering the possibility of inadvertent lane exits, this function significantly improves driving safety, especially in scenarios when a driver’s attention may be diverted. Because of this, Lane Assist helps reduce the number of accidents that come from drifting out of lanes, which may be especially important on highways or lengthy trips when drowsiness sets in.
To analyze road markings and identify lane deviations, Lane Assist depends on clever algorithms and real-time data processing. The technology notifies the driver by visual, aural, or tactile feedback when it detects possible lane departure without signaling, allowing them to take appropriate action. Moreover, in certain sophisticated configurations. Lane Assist can automatically apply a steering force to gently guide the car back into its lane. This integration of safety and technology highlights both the advancement of contemporary cars and a significant step in the direction of more dependable and safe driving.







2 Comments